MILKI PSY Prototypes
The MILKI-PSY consortium has developed a range of research prototypes, including the MILKI-PSY Cloud, an ML-based cloud solution for processing multimodal sensor streams and delivering psychomotor feedback. The IMPECT framework serves as an immersive training environment for various psychomotor skills like dance and exercise, featuring a virtual teacher, feedback cards, and a cloud server for session management. Another prototype is a multiplayer exergame that tracks body movements in real-time using Human Pose Estimation technology. We’ve also developed visual feedback systems using AR and XR, such as a virtual golf club for real-time skill comparison and training, as well as an augmented reality application that supports human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks. Additionally, we’ve researched methods like prototype networks and attention mechanisms for few-shot learning to identify and evaluate movement discrepancies in student training sessions.
MILKI PSY Cloud
Partner / Lead: RWTH
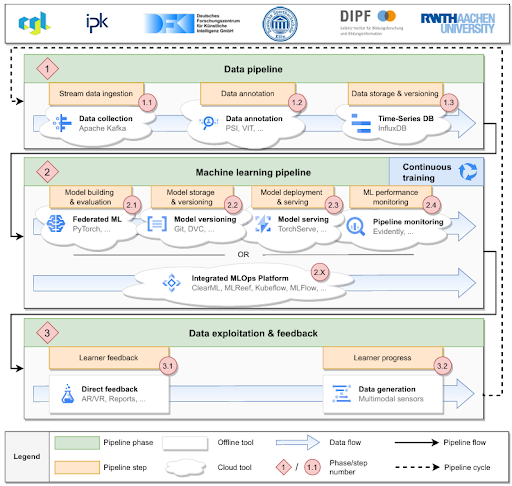
MILKI-PSY Cloud is a collaborative ML-based cloud solution for processing multimodal sensor streams and delivering feedback in psychomotor learning scenarios. Structured in three phases — data ingestion, machine learning, and data exploitation — it applies MLOps approaches to provide both direct and long-term feedback.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Immersive Multimodal Psychomotor Environments for
Competence Training (IMPECT)
Partner / Lead: CGL
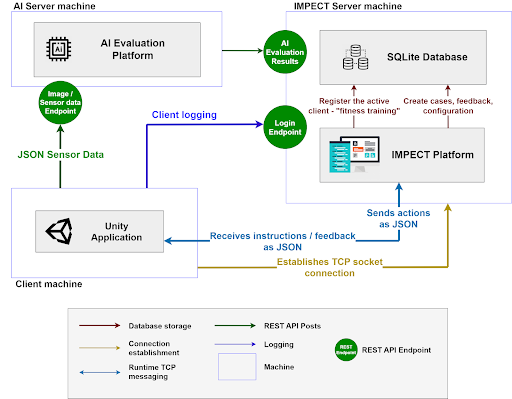
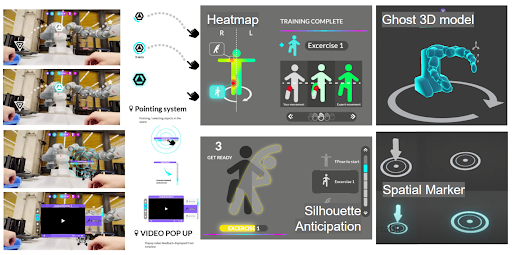
A training toolkit designed for psychomotor skills training, consisting of feedback and instructional components. It includes the IMPECT front-end, a client application that serves as an immersive learning environment for training psychomotor skills, and the IMPECT-Server, a cloud server used to navigate learning sessions and generate feedback cards for the client application. Multiple front-end client applications can connect to the IMPECT-Server to support a range of psychomotor skills (e.g., dance, exercise, human-robot interaction, etc.)
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Dynamic Movement Primitives
Partner / Lead: DFKI
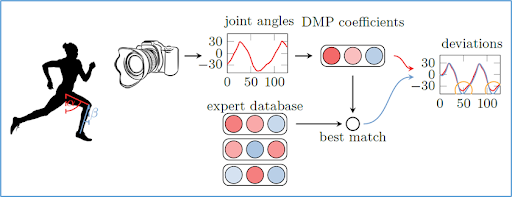
DFKI investigated and implemented several methods to efficiently represent and predict human motion. We outlined a machine learning supported approach to provide feedback. For the walking scenario, we provided an evaluation of how movements can be compared to show deviations between student and expert movement. DFKI also provided initial software modules for motion representation and motion comparison for the partners to support prototype development.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
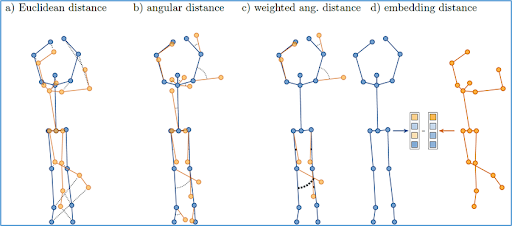
Few-shot keypose detection
Partner / Lead: DFKI
We investigated methods to automatically recognize student trials for poses with only a single correct teacher demonstration. We investigated relevance learning, prototype networks, and attentional mechanisms to achieve a robust few-shot approach that generalizes to all students. In an experiment with one teacher and 27 students performing a sequence of fitness and dance movement elements, we showed that prototype networks work best in combination with an attention mechanism.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Motion visualization techniques
Partner / Lead: RWTH
This application investigates and researches comparative visualization techniques for human movements, providing different visualization types to display body movements and error information. It supports showing one action at a time while considering changes over time to analyze factors influencing motion visualization techniques and aid in movement correction.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)


Fitness Trainer
Partner / Lead: DFKI
We present a system for monitoring exercise performance and immediate feedback on posture during training. This real-time guidance facilitates self-correction and boosts motivation, especially without professional supervision. Fitsight is a reliable and sophisticated tool for self-guided fitness journeys.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Motion skeleton superimposition in dancing/fitness
Partner / Lead: DSHS
Visualisation method to provide real-time feedback for learning a movement sequence (e.g., in the field of dance and fitness). The targeted performance (teacher) is virtually and proportionally superimposed with the actual performance (learner) via a large screen during learning.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)

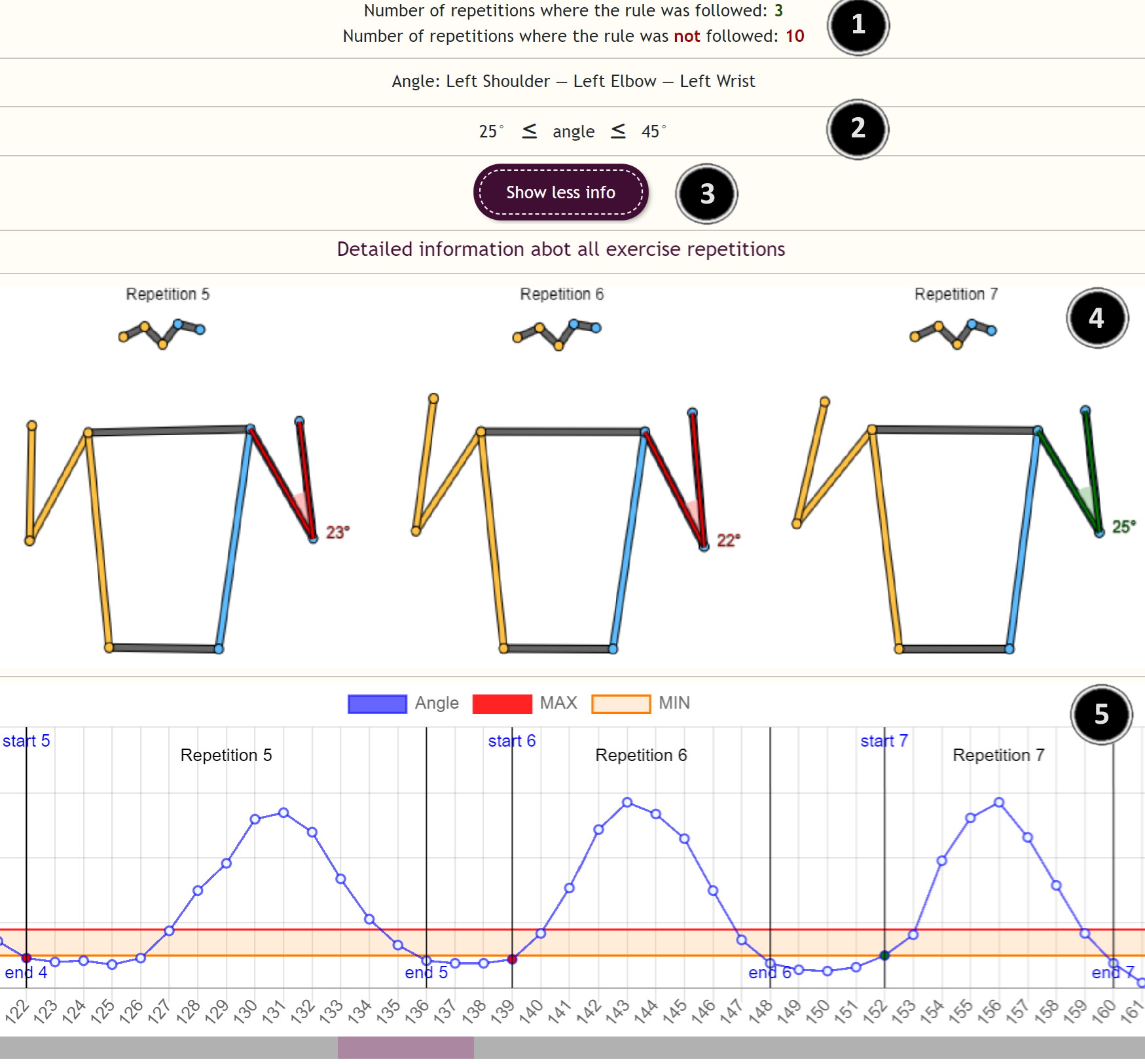
Psychomotor Feedback Engine
Partner / Lead: RWTH
A rule-driven feedback engine for psychomotor learning to create rules input by domain experts to provide real-time, personalised feedback. The system dynamically applies these rules based on continuous analysis of user movements, timing, and accuracy, without relying on hardcoded rules or labelled datasets.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
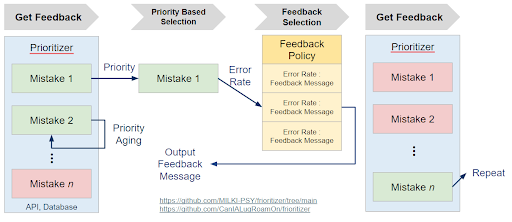
Feedback/Error Prioritisation
Partner / Lead: DIPF
An implementation with REST API to set up and schedule feedback pipelines based on preset priorities.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
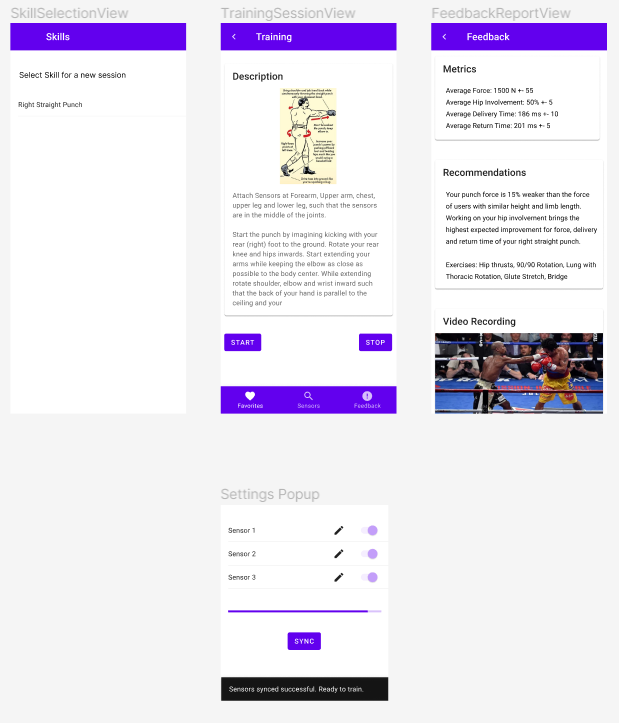
[WIP] Dot sensor application
Partner / Lead: DIPF
Mobile Application that uses human keypoint estimation and senors to implement velocity based training method for psychomotor skill improvement
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
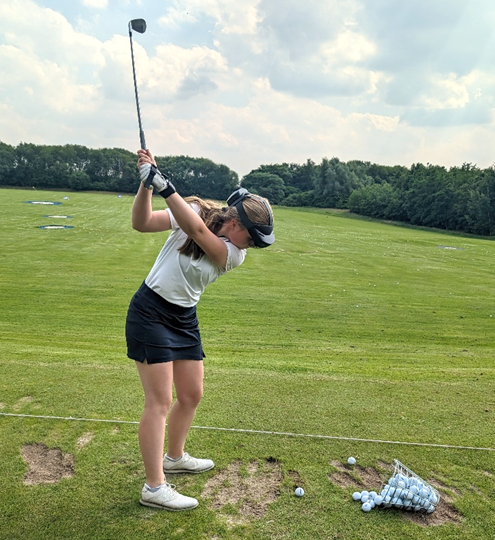
GolfPutt AR Tool
Partner / Lead: DSHS
Virtual golf club as a role model for learning the golf putt. It is superimposed with the real golf club of the learner in real-time via Microsoft HoloLens glasses.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
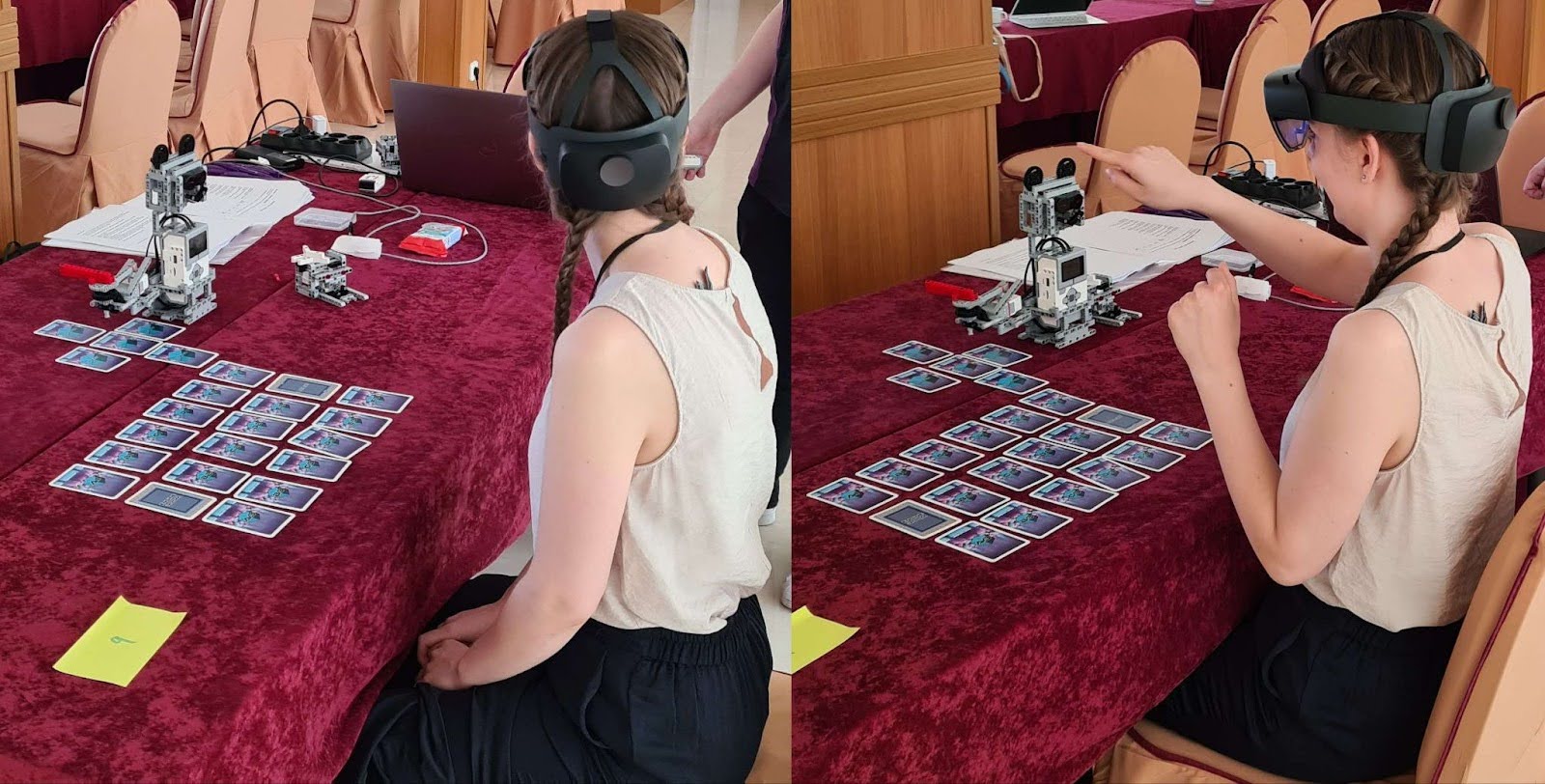


IMPECT robots escape room
Partner / Lead: CGL
This study investigates human-robot interaction within an educational setting, emphasizing trust and collaborative decision-making facilitated through augmented reality (AR) technology. Participants were tasked with repairing robot components and navigating a game-like environment with an AR device. The study aimed to understand how trust is established and maintained in interactions with autonomous robots.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
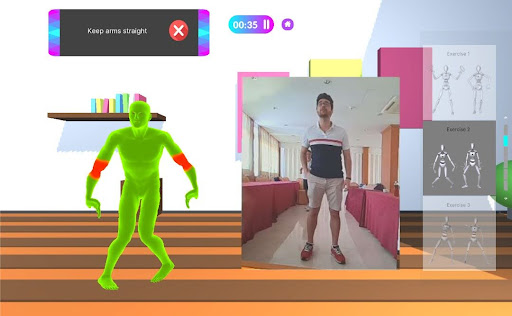
IMPECT-Dance – Wizard of Oz
Partner / Lead: CGL
One of IMPECT’s front-end client applications, an immersive learning environment for a full-dance routine consisting of five exercises with a Wizard of Oz study where the expert navigates sessions using the IMPECT’s backend platform locally. It features multimodal feedback delivered through feedback cards, a virtual teacher with recorded movements from a motion capture suit, and a live camera view using a webcam
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
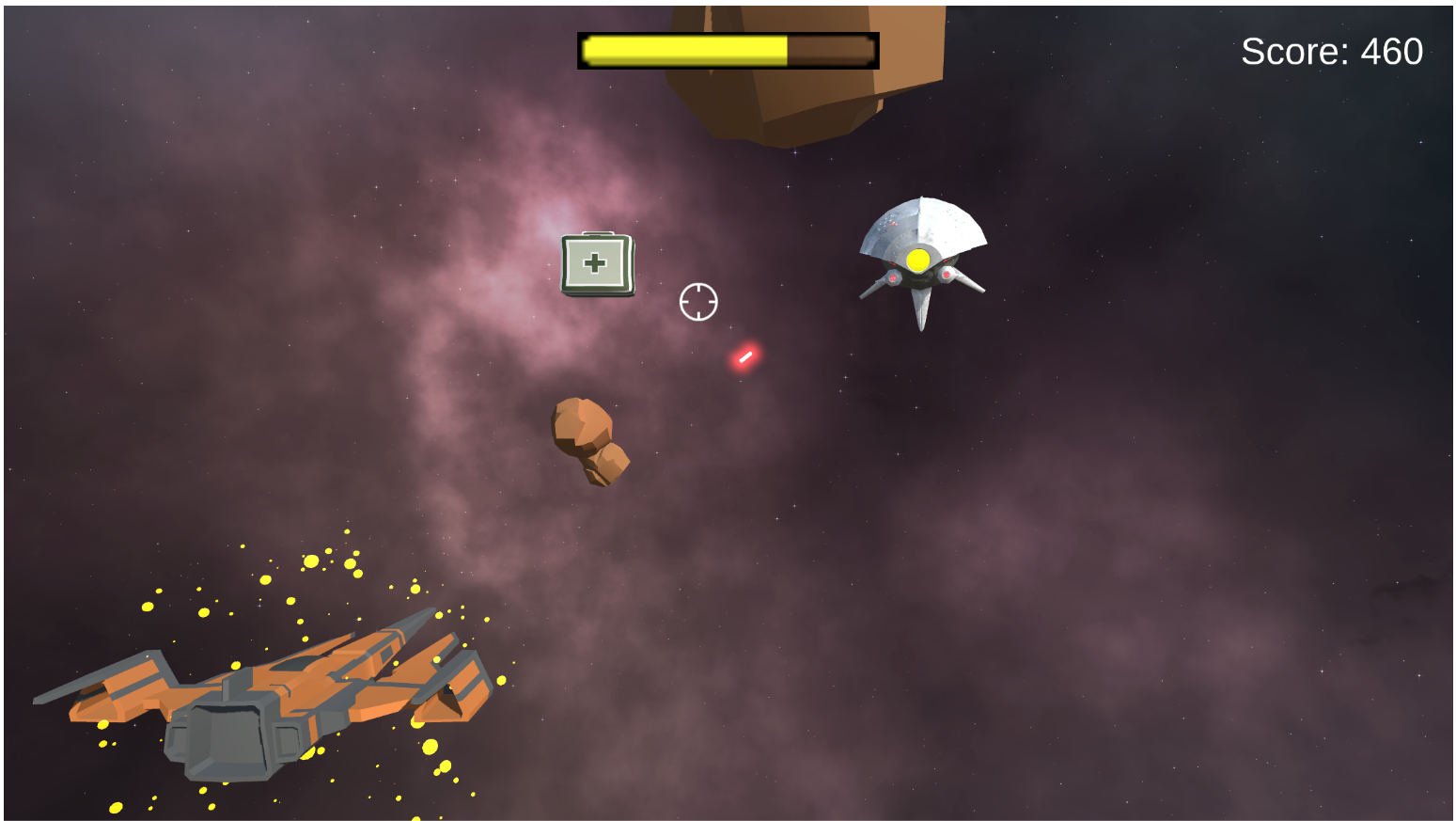
Space Striker: Exercise Odyssey
Partner / Lead: RWTH
This prototype application is a multiplayer exergame where two players cooperate to control a spaceship through body movements, navigating an asteroid field and escaping enemies. The game uses Human Pose Estimation (HPE) technology to track body movements in real-time, requiring no specialized hardware.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Mathkinetics
Partner / Lead: DIPF
A video game that employs pose and speech recognition, challenging users to navigate obstacles while solving arithmetic problems.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
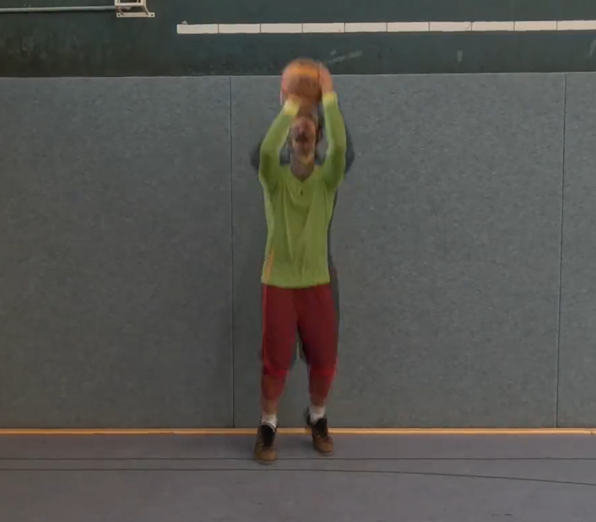
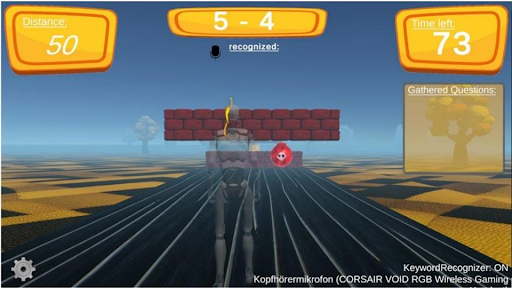

Motion anticipation in basketball
Partner / Lead: DSHS
Superimposed videos are used to help learners anticipate shots and fakes in basketball. In these videos, a superimposed shot and fake are shown, stopping just before the ball is released or at the peak of the fake to conceal the outcome. After viewing, learners identify whether the player in a specific coloured shirt performed a shot or a fake. The superimposed motions aim to facilitate easier comparison and identification of differences between the actions.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Golfpitch visual and tactile feedback tool
Partner / Lead: DSHS
A novel learning method for golf pitch training includes augmented visual information through XR. A virtual hand and wrist of an expert is shown in real-time through Microsoft HoloLens glasses. Learners try to follow the optimized wrist motion both in slow motion and in normal speed.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)

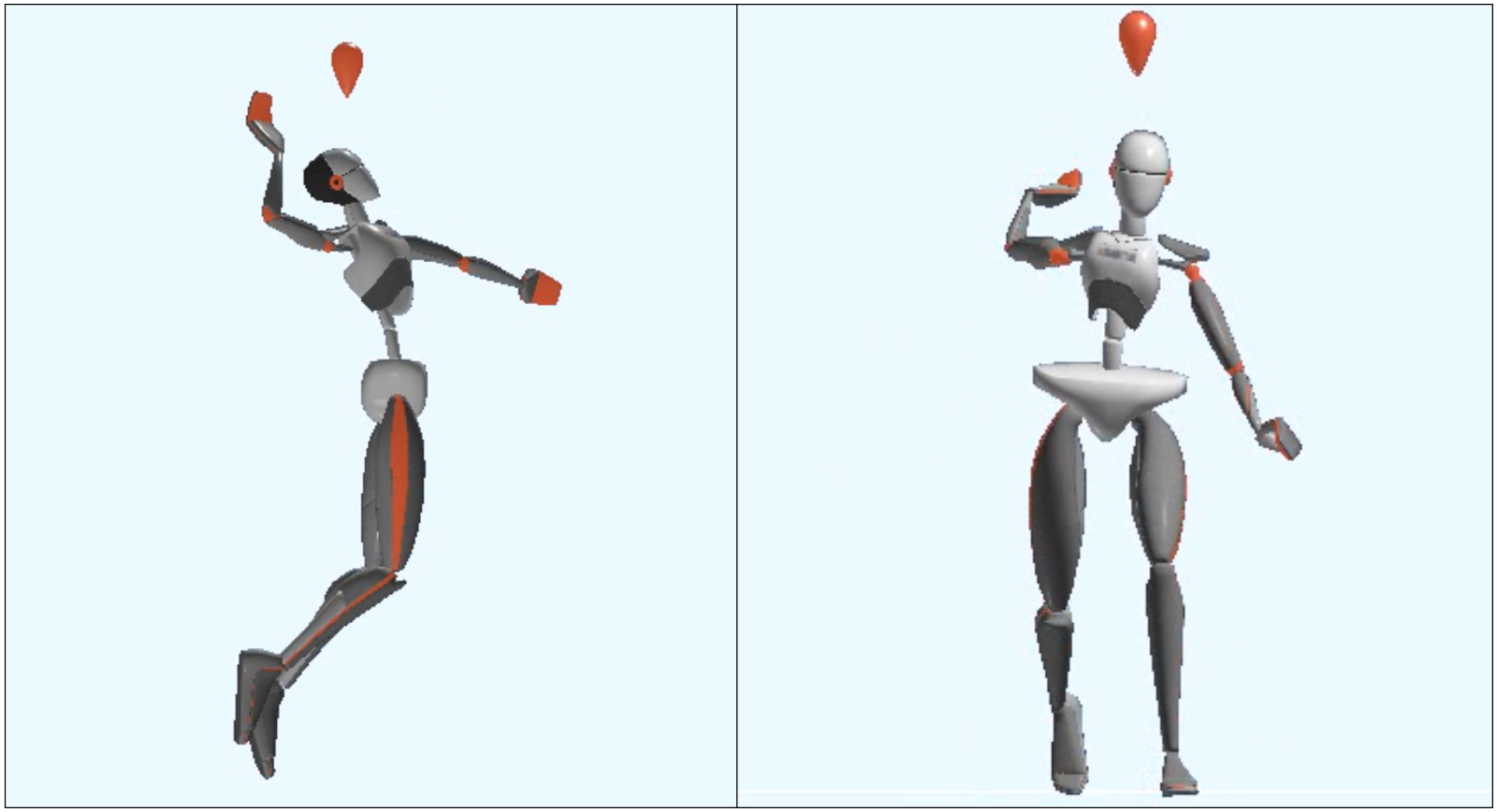
XSens Motion comparison (DTW/Kabsch)
Partner / Lead: DSHS / RWTH
A novel approach for identifying motion differences in sports training using sensor suit data to visually compare joint positions as skeletons against reference values. By calculating root-mean-square deviation (RMSD), it quantifies differences in body positions. After manually aligning recordings at key motion points, the Kabsch algorithm adjusts orientation and translation to minimize RMSD. Frame-by-frame analysis of minimal RMSD reveals motion dissimilarities.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
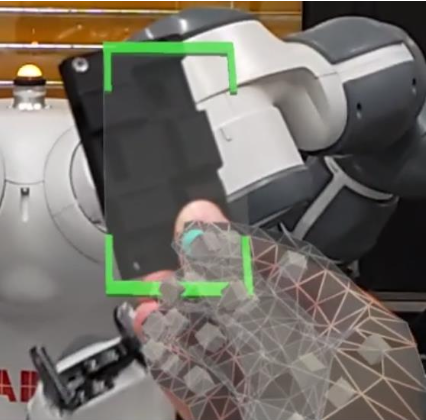
Human ↹ Robot object handover
Partner / Lead: IPK
An approach to explore how a robot nonverbally communicates motion intentions in a collaborative work environment. The proposed setup involves enhancing a collaborative assembly cell, featuring the two-armed robot Yumi, with the use of Microsoft HoloLens.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)



Collaborative assembly with robots in AR/VR
Partner / Lead: IPK
An approach for designing a framework for AR-based and VR-based training systems aimed at acquiring psychomotor skills in a collaborative assembly scenario.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Hololens Hand Capture
Partner / Lead: IPK
An extended version of the AR application for the handover task now includes hand tracking. The goal is to transmit the human hand’s coordinates to the robot controller, enabling the robot to synchronize its end effector accordingly.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
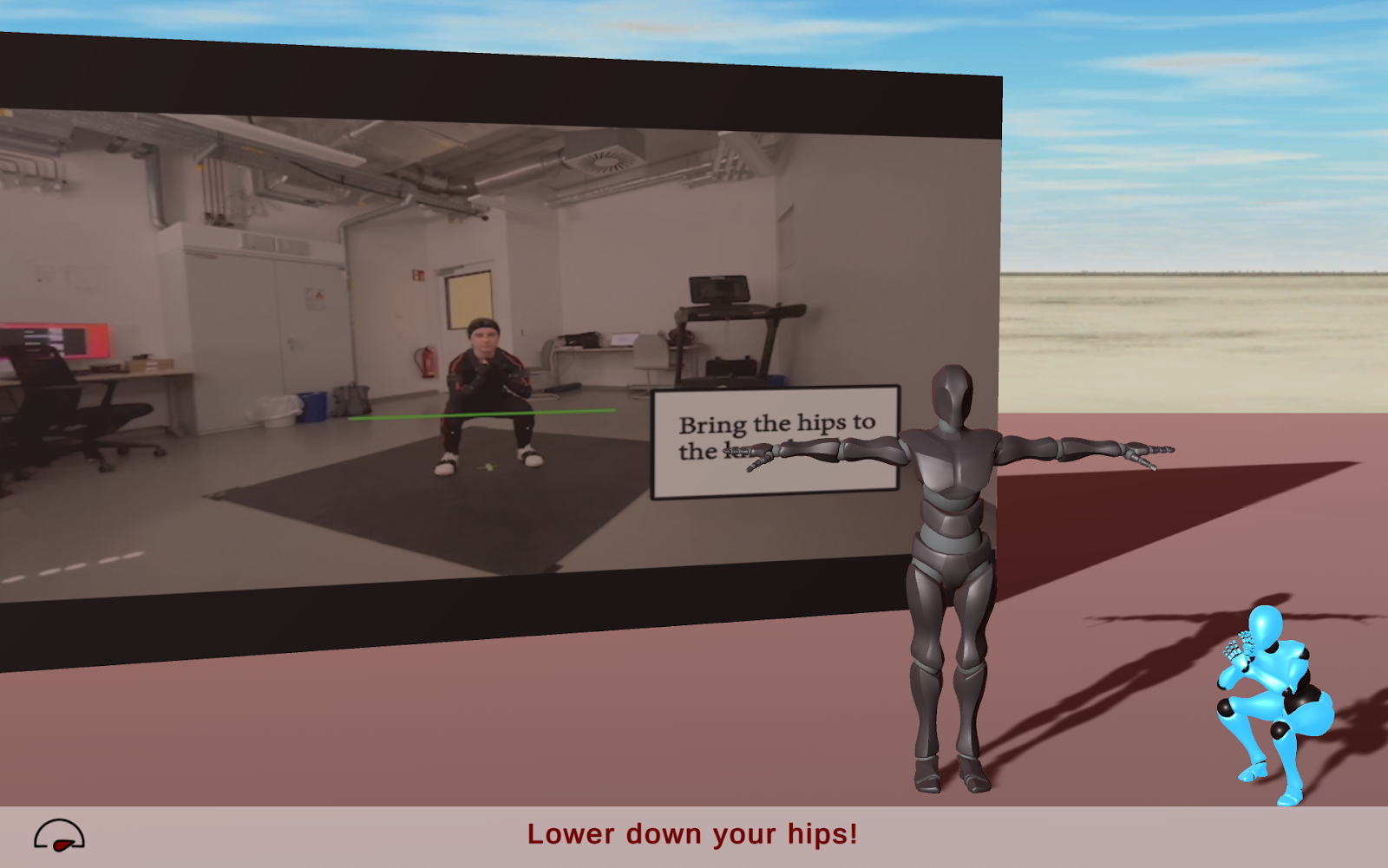

IMPECT-Sports – Wizard of Oz
(Exercise routine)
Partner / Lead: CGL
This prototype utilizes IMPECT components, an immersive learning environment for basic exercise movements where a Wizard of Oz study was conducted to allow the teacher to navigate sessions from the local machine by triggering multimodal feedback (e.g., visual, auditory). It features a virtual teacher with recorded movements using a motion capture suit and real-time motion recording of participants via Kinect.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Edutex
Partner / Lead: DIPF
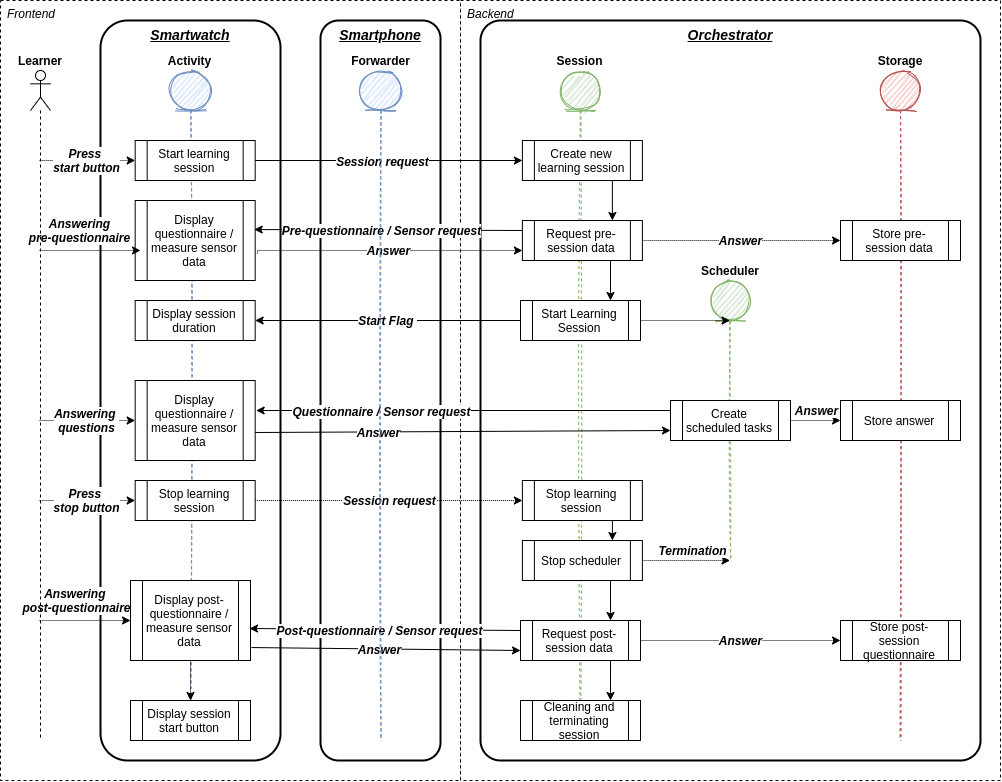
The Edutex software infrastructure allows learning analytics stakeholders to leverage data related to learners‘ physical contexts. Edutex accomplishes this by utilizing sensor data from smartphones and smartwatches, along with response data from experience samples and questionnaires collected via learners‘ smartwatches.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)

IMPECT robots for
assembly and handover
Partner / Lead: CGL
This study explores immersive learning in the field of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). We examine four categories of HRI cases: robot-led, human-led, autonomous, and collaborative. For each case, we evaluate the potential risks and human learning outcomes. Our findings include interaction styles that can be applied in HRI as well as the directionality and (multi)modality of these interaction styles.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
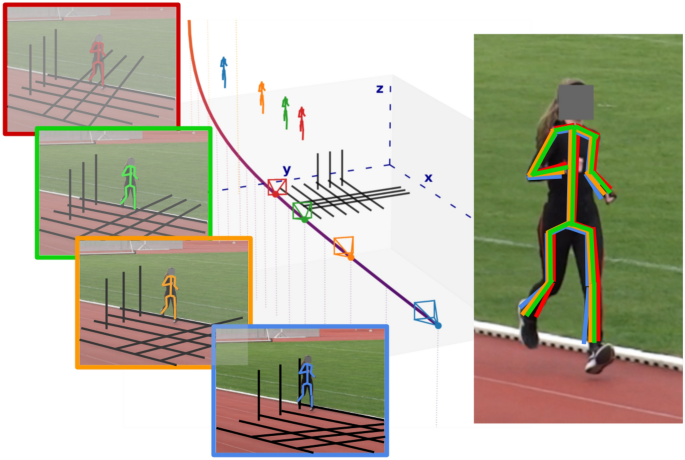
3D Pose Estimation in Sports Broadcast
Partner / Lead: DFKI/DSHS
DFKI and DSHS have proposed a method to estimate the global geometry of athletics stadium images using track boundaries. By back-projecting estimated 3D skeletons into the image using this global geometry, we were able to show that current state-of-the-art 3D methods for estimating human posture are not (yet) accurate enough to be used in kinematics research.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
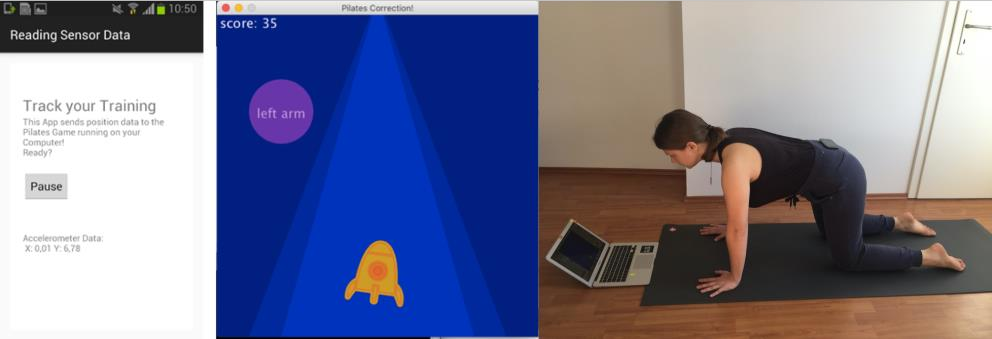
Pilates Correction
Partner / Lead: DIPF
A game which enables users to perform a basic Pilates exercise while playing, with their score determined by how accurately they execute the exercise.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Mental Training: Running VR
Partner / Lead: DIPF
A Cognitive Behavioral-influenced VR application that integrates two key mental aspects of running—strategy and motivation—in the context of long-distance races. The application, designed for head-mounted displays, allows users to simulate typical racing scenarios without the need for physical running.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
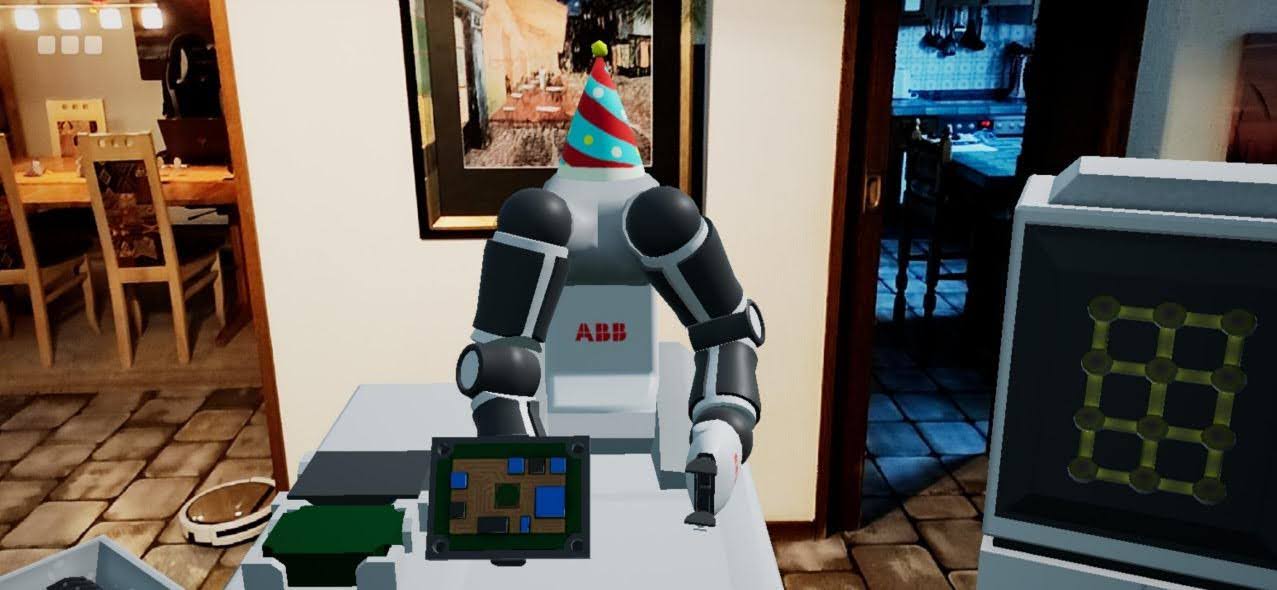


Yu & Mi
Partner / Lead: CGL
An AR application for training human-robot interaction, featuring a step-by-step assembly case completed in collaboration with a virtual robot. Instructional and feedback components are provided by the virtual robot to assist the user throughout the assembly process.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
Flowmotion
(Yoga Training Environment)
Partner / Lead: CGL
An immersive learning environment designed to teach basic Yoga postures, featuring a camera-based system that tracks the user’s skeleton using ThreeDPose UnityBarracuda for 3D pose estimation. A virtual teacher demonstrates the postures, with corrective feedback provided for errors and positive feedback given as score points.
Read More (doi, ref, URL, …)
